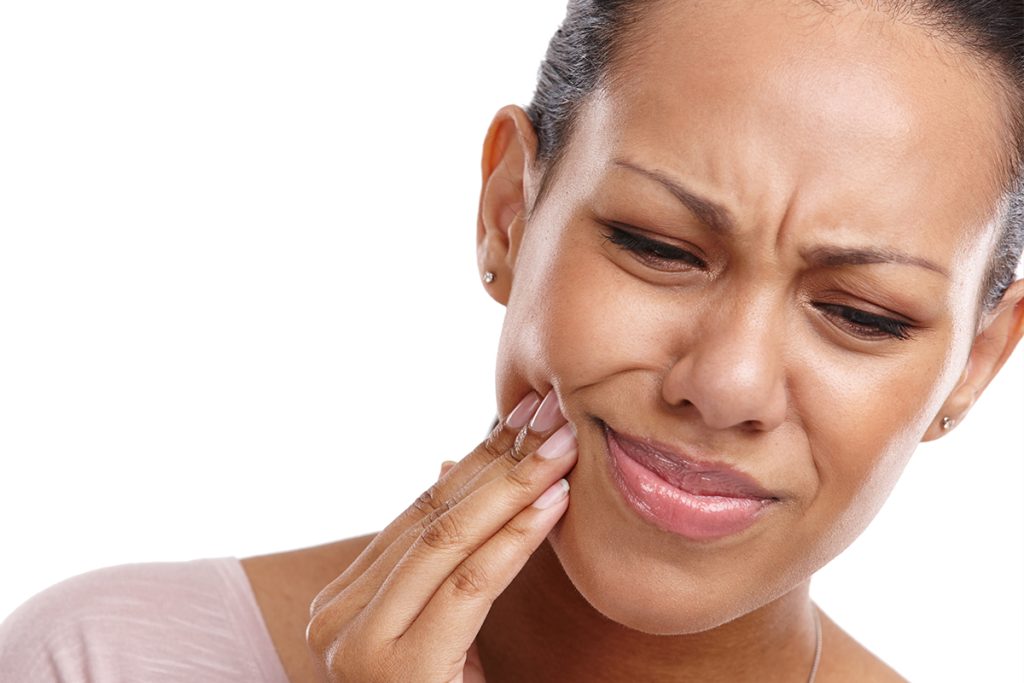
Toothaches are among the most common dental complaints, but they can be indicative of a wide range of underlying dental issues. While toothaches are often caused by cavities, they may also be a result of gum disease, infections, or even dental trauma. Whether the pain is sharp or dull, constant or intermittent, it’s crucial to address the issue quickly. Ignoring a toothache can lead to more serious problems, including infections that may spread to other areas of the mouth or body. Immediate care is essential not only to relieve the pain but also to prevent long-term damage to your teeth and gums.
Common Causes of Toothaches
There are several reasons why you might experience a toothache. The most common cause is a cavity, where bacteria have damaged the tooth’s enamel, leading to sensitivity or pain. Other causes of toothaches include tooth abscesses, which are infections that occur at the root of the tooth, gum disease, cracked teeth, or exposed tooth roots. Occasionally, toothaches may be linked to jaw problems, like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Identifying the root cause of the pain is essential in determining the proper treatment to relieve the discomfort and prevent further issues.
Treating Toothaches
Cavity Treatment (Fillings)
A cavity is one of the most common causes of toothaches, and it occurs when bacteria break down the enamel of the tooth. The pain associated with a cavity can range from mild sensitivity to sharp, constant pain. The treatment for a cavity typically involves removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling it with a material such as composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain. This not only relieves the pain but also restores the tooth’s function and prevents further decay. Regular check-ups are important to detect cavities early before they become severe.
Root Canal Therapy
If a toothache is caused by infection in the tooth’s pulp, a root canal may be necessary to save the tooth and relieve the pain. A root canal procedure involves removing the infected tissue from the center of the tooth and cleaning the area before sealing it with a special material. This treatment is typically required for severe toothaches caused by deep infections, abscesses, or trauma. While it may sound intimidating, a root canal is an effective way to save a tooth and stop the pain, allowing you to keep your natural teeth intact.
Tooth Extraction
In some cases, a toothache may be so severe that extraction is the only viable option. This is typically the case when the tooth is irreparably damaged by decay, trauma, or infection. A tooth extraction removes the affected tooth, alleviating the pain and preventing further infection. Once the tooth is removed, options such as dental implants or bridges can be discussed to replace the lost tooth and restore function and aesthetics to your smile. Extraction is usually considered a last resort when other treatments are not possible.
Gum Disease Treatment
Gum disease is another common cause of toothaches. If bacteria have caused inflammation or infection in the gums, it can lead to pain and discomfort around the affected teeth. Treating gum disease typically involves professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline. In more advanced cases, scaling and root planing may be necessary to smooth the tooth roots and remove infected tissue. Addressing gum disease early is crucial to avoid tooth loss and prevent the condition from progressing into more severe stages.
Dental Abscess Treatment
A dental abscess occurs when an infection develops at the root of a tooth, causing intense pain. Abscesses can lead to swelling, fever, and even the spreading of the infection to other parts of the body if left untreated. Treatment for an abscess typically involves draining the infection, cleaning the affected area, and prescribing antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria. In some cases, a root canal or tooth extraction may be necessary to remove the infection and prevent further complications.
Cracked or Chipped Tooth Repair
A cracked or chipped tooth can cause sharp, sudden pain, especially when biting or chewing. If left untreated, a cracked tooth can worsen over time, potentially leading to infection or the need for extraction. Depending on the severity of the crack, treatments such as dental bonding, crowns, or veneers may be used to restore the tooth’s function and appearance. Repairing a cracked tooth promptly helps prevent further damage and alleviates the associated pain.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Treatment
In some cases, tooth pain may not be directly related to the teeth themselves but to problems with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jaw to the skull. TMJ disorders can cause toothaches, jaw pain, headaches, and difficulty moving the jaw. Treatment for TMJ disorders may include wearing a night guard to prevent teeth grinding, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgery. By addressing the root cause of the pain, TMJ treatments can help relieve toothache symptoms and improve overall jaw function.
Preventive Care to Avoid Future Toothaches
Once a toothache is treated, it’s important to take steps to prevent future occurrences. Regular dental check-ups allow the dentist to detect issues like cavities or gum disease before they progress into painful problems. Practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash, is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing toothaches. A balanced diet that limits sugary foods can also help protect teeth from decay and cavities. With the right preventive care, you can minimize the risk of future toothaches and keep your smile healthy for years to come.